In silico characterization and various biological activities reported for Passiflora Incarnate Linn.
Hemant Chikhale*, Sakshi Deshpande, Trupti Dhande, Purvaa Ingale and Sourav Suryawanshi
Published Date: 2022-09-13Hemant Chikhale1*, Sakshi Deshpande2, Trupti Dhande2, Purvaa Ingale2and Sourav Suryawanshi2
1Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Savitribai Phule Pune University, Pune, India
2Department of Pharmacy, Savitribai Phule Pune University, Pune, India
- *Corresponding Author:
- Hemant Chikhale Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Savitribai Phule Pune University, Pune, India, Tel: 9405211956; E-mail:hemantch558@gmail.com
Received date: July 06, 2022, Manuscript No. IPJSVP-22-13979; Editor assigned date: July 11, 2022, PreQC No IPJSVP-22-13979 (PQ); Reviewed date: July 25, 2022, QC No. IPJSVP-22-13979; Revised date: September 06, 2022, Manuscript No. IPJSVP-22-13979 (R); Published date: September 13, 2022, DOI: 2469-6692.8.6.001
Citation: Chikhale H, Deshpande S, Dhande T, Ingale P, Suryawanshi S (2022) In Silico Characterization and Various Biological Activities Reported for Passiflora incarnate linn. J Silico In Vitro Pharmacol Vol:8 No:6
Abstract
Based on the survey for, the number of patients and medical practitioners in the industrialized world which use herbal medicines as a supplement to or substitute for prescription drugs are increased. Herbal medicines are o ten considered to be a gentle and safe alternative to synthetic drugs. More than half of the medically important pharmaceutical drugs are either natural products or derivatives of natural products. Passiflora incarnata (Passifloraceae; passion lower family)i s an important medicinal plant of tropical and subtropical India. Its medicinal remedies such as sedative, anxiety and hypertension are reported in traditional systems of medicine such as Ayurveda, Siddha and Unani. This article focuses on the in silico approach to study phytopharmacologically active compound and there in silico properties for the direction to further research in the field of pharmaceuticals.
Keywords
In silico approach; Herbal medicine; Medicinal remedies; Bioactive compound; Passiflora incarnate Linn
Introduction
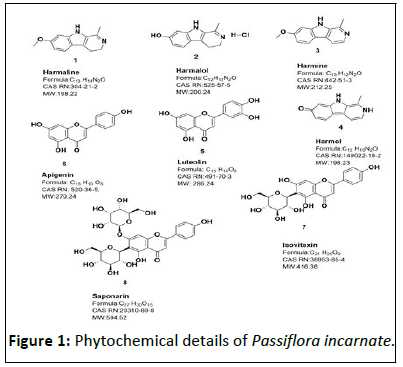
Maypop, apricot vine, passion vine, and granadilla are all names for passion flower. It develops with a thick, woody stem it can grow up to 30 feet (10 meters) tall. The genus Passiflora contains 500 species, the mainstream of which are originating in warm and tropical climates. Passiflora comes from Latin word “Passio” that was first time revealed by Spanish discoverers in 1529 and was described as a symbol for “Passion of Christ” [1]. This plant has long olden times of use in traditional medicine in West India, Mexico, the Netherlands, South America, Italy, and Argentina. One of species of this genus named as Passiflora incarnata is more popular than its other species. Passiflora contains several compounds together with alkaloids, phenols, glycol flavonoids and cyanogenic compounds. The main chemical constituents of the Passion flower are the flavonoids (0.25 percent) such as vitexin, isovitexin, orientin, isoorientin, apigenin, kaempferol and quercetin. Harman, harmin, harmalin, harmol, and harmalol are examples of indole alkaloids (0.1 percent) based on the beta carboline ring system. Other isolated plant constituents include glycosides, carbohydrates, amino acids, benzopyrones, cyanogenic glycosides like gyanocardin, and pyrone derivatives like maltol and ethyl maltol. Two imperative constituents like chrysin and tri substituted Benzo lavone moiety (BZF) have been inaccessible [2-4]. In this paper we are focusing on the chemical constituents and there in silico properties for the outlook research work.
Materials and Methods
Chemical constituent: The most widespread active constituent of Passi ora incarnate include alkaloids, phenols, glycosyl lavonoids, and cyanogenic. The lavonoids represent about 0.25 percent including vitexin, isovitexin, orientin, isoorientin, apigenin, kaempferol, and quercetin are the primary chemical elements of the passion lower. Other like harman, harmin, harmalin, harmol, and harmalol are indole alkaloids having 0.1% that based on the beta carboline ring system. Consecutively glycosides, sugars, amino acids, benzopyrones, cyanogenic glycosides like gyanocardin, and pyrone derivatives such as maltol and ethyl maltol are some of the other isolated plant ingredients [5-7]. Chrysin and the tri substituted Benzo lavone moiety (BZF) are two key ingredients that have been well known [8,9].
Bioactive compounds: The chemical composition of Passi ora species is in the same way poorly unwritten. Researchers diverge on what causes its tranquillizing e ects: indole alkaloids such harmane, harmaline, and harmol; lavonoids like apigenin, luteolin, and scopoletin; or an isolated tri substituted benzo lavone. Furthermore, it was in recent times exposed that Passiflora has more Gamma Amino Butyric Acid (GABA) than the 20 other plants tested. Passiflorine, one of six isolated alkaloids from P. incarnata, is consideration by some to be the plants active ingredient, regardless of being listed as inert on the agricultural research service website. , a steroid like chemical isolated from P. edulis stems and leaves but not an alkaloid, is the only equivalent entry in the chemical abstract service database. P. incarnata or P. alata aerial portions, harvested during the flowering and fruiting phase, are used to make passionflower extracts. Thin layer chromatography, microscopic and macroscopical inspection, and organoleptic analysis are used to validate the botanical identity of an object. Indole alkaloids, primarily harman, harmaline, and harmine, coumarin derivatives, cyanogenic glycosides (gynocardin), amino acids (including GABA), fatty acids (linoleic and linolenic), gum, maltol, phytosterols (stigmasterol), sugars (sucrose), a trace amount of volatile oil, vitexin, isovitexin, and their C-glycoside (Figure 1) [10,11].
In silico Study of herbal compound: The creation of software based on bioinformatics and chemo informatics algorithms has made it possible to conduct in silico examinations of compounds with medicinal potential. Working with many molecules is made possible by the programmes and software used, which reduces the amount of animal testing, research costs, and time spent on the study. Additionally, they may serve as an addition to experimental research methods including in vivo, ex vivo, and in vitro. Our understanding of molecular pathways has substantially enhanced as a result of the discovery and development of novel active ingredients or pharmaceuticals utilizing these computational tools. This has also given us the opportunity to recommend new treatment options for a number of diseases. Numerous in silico techniques are used in chemo informatics to forecast the pharmacokinetic and physicochemical characteristics of compounds based on their chemical structure. In this paper by using the SwissADME web tool, the pharmacokinetic parameters or drug like features of the chosen substances were identified. The active components of Passiflora embody the following drug likeness parameters in the current study to show their pharmaceutical fidelity, including lipophilicity (LogP), the number of hydrogen bond acceptors, the number of hydrogen bond donors, Topological Polar Surface Area (TPSA), and the number of Rotatable Bonds (nRB) based on Lipinski's rules (Table 1).
| Compound Code |
No. of H-bond donors | No. of H-bond acceptors |
XLogP | TPSA | Pharmacokinetics | Number of Rotatable Bonds (nRB) | Lipinski violation |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBB | GI | |||||||
| 1 | 1 | 2 | 2.07 | 37.38Ų | Yes | High | 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 1.75 | 48.38Ų | Yes | High | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 | 3.74 | 37.91 Ų | Yes | High | 1 | 0 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 0.75 | 48.65 Ų | Yes | High | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 4 | 6 | 2.53 | 111.13Ų | No | High | 1 | 0 |
| 6 | 3 | 5 | 3.02 | 90.90 Ų | No | High | 1 | 0 |
| 7 | 7 | 10 | 0.21 | 181.05Ų | No | Low | 3 | 1 |
| 8 | 10 | 15 | -1.6 | 260.20Ų | No | Low | 6 | 3 |
Table 1: Pharmacokinetic and physicochemical characteristics of compounds based on their chemical structure using the SwissADME web tool.
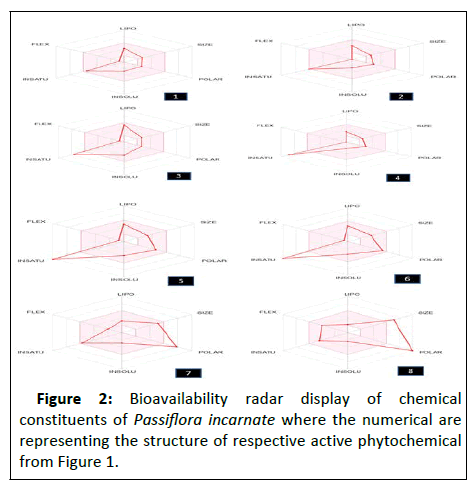
Biological RADAR graph: Bioavailability radar display allows for a quick assessment of drug likeness. Lipophilicity, size, polarity, solubility, flexibility, and saturation are six physicochemical characteristics that are taken into consideration. Descriptors from were used to construct a physicochemical range on each axis, which is shown as a pink area, and in which the radar plot of the molecule must completely fall to be deemed drug like. The pink region denotes the ideal range for each property (Lipophilicity: XLOGP3 between 0.7 and +5.0, Size: MW between 150 and 500 g/mol, polarity: TPSA between 20 and 130 2, Solubility: log S not higher than 6, Saturation: fraction of carbons in the sp3 hybridization not less than 0.25, and Flexibility: no more than 9 rotatable bonds). Because the chemical in this instance is excessively flexible and polar, oral bioavailability is projected to be low (Figure 2) [12].
Pre ADMET study: The desirable pharmacokinetic characteristics of the molecules are also regarded as a key component since they should lead to optimal Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion (ADME). Clinical trial failure may be caused by a poor ADME profile. Therefore, the successful development of candidate small compounds depends on early and precise ADME profiling during the discovery phase.
Results and Discussion
A pharmacological compound's efficacy and safety are key considerations when deciding whether to put it on the market, and Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion (ADME) profiling can take these considerations into account. Due to the failure of 60% of therapeutic compounds during the drug development process, ADME characteristics play a significant role. The expense of drug research would be significantly reduced if these characteristics could be predicted early on. The human colon cancer cell permeability test (Caco-2) has evolved into one of the most widely used methods for examining how well a medicine is absorbed by the human body [13]. According to this last parameter, several laboratories classify the substances for therapeutic purposes using the following standards: Values between 20 and 80 nm/s predict moderate transcellular absorption in vivo (20 to 80% of the absorbed fraction) while values between 80 and 100 nm/s predict strong transcellular absorption in vivo. Values 20 nm/s predict poor transcellular absorption in vivo (fraction of 0 to 20% absorbed) (80 to 100 percent of the fraction absorbed fraction) (Table 2) [14,15].
| Compound code | Caco-2 Cell permeability | MDCK Cell permeability | HIA Absorption | Plasma protein binding |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 42.2101 | 317.19 | 92.82745 | 64.05014 |
| 2 | 10.0725 | 285.974 | 88.79656 | 59.56586 |
| 3 | 33.068 | 317.19 | 92.82746 | 56.6758 |
| 4 | 10.5468 | 44.302 | 88.12284 | 97.25341 |
| 5 | 4.53973 | 36.5205 | 79.42723 | 99.71723 |
| 6 | 21.3306 | 1.2844 | 94.26301 | 25.58905 |
| 7 | 10.4277 | 0.045505 | 3.387752 | 39.96231 |
| 8 | 12.8498 | 1.15043 | 57.26455 | 67.77041 |
Table 2: Pre ADMET study of phytochemical of Passiflora incarnata, where the numerical are representing the structure of respective active phytochemical from Figure 1.
Pharmacological activity: Plant can be an excellent source of pharmaceutical compound, but their bioactive molecule often complex or difficult to synthesize. The synthesis procedures are expensive and laborious. The impediment in the synthesis process made extraction of compound from natural sources critical and led researcher to search for and eventually discover a closely related analogue in seeds, leaves, bark, stem, and fruit respectively. Passiflora incarnate is such a type of plant with pharmaceutically significant extract, approximately 500 passiflora species has been most extensively studied for its pharmacological effect. In some experiments, it has potential effects for treatment of some diseases like anxiety, opiates withdrawal, insomnia, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and cancer. It also has antispasmodic and mild anti-microbial effects that are known. Also, recent study showed that leaves of it had anticonvulsant effects. In this paper, we have included
• Hypertension: Shown by species P. incarnata, P. nepalensis
• Anti-convulsant: Shown by species P. incarnata
• Anti-anxiety: Shown by P. incarnata
• Anti-cancer: Shown by P. incarnata
• Sexual dysfunction: Shown by P. incarnata
• Anti-microbial: Shown by P. incarnata
• Anti-oxidant: Shown by P. nitida, P. palmeri, P. foetida
• Anti-Inflammatory: shown by P. edulis
• Anti-Tumour: shown by P. edulis
• Congestive heart failure: Shown by P. incarnata
Hypertension: Despite advances in pharmacotherapies and mechanical treatments, cardiovascular disease continues to be a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, with every indication that the burden will grow. P. incarnata, an allied species of P. nepalensis, has previously been reported to have antihypertensive properties. P. incarnata's antihypertensive consequence is due to the incidence of a water soluble substance inaccessible as a mercury salt (C10H22O8NHgCl2) and flavonoids. P. nepalensis is used in folklore medicine for treating hypertension. Plants can be an excellent source of pharmaceutical compounds, but their bioactive molecules are recurrently complex or difficult to synthesize [16]. The synthesis procedures are both expensive and time consuming. The obstruction in the synthesis process made extraction of the compound as of natural sources critical, prompting researchers to look for and ultimately discover a closely related analogue in seeds, leaves, bark, stem, and fruit. Passiflora incarnata is a type of plant with pharmaceutically noteworthy extract, and approximately 500 Passiflora species have been comprehensively studied for their pharmacological effect. In some studies, it has revealed undertake in the treatment of diseases such as anxiety, opiate withdrawal, insomnia, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, and cancer. It also has antispasmodic and mild antimicrobial properties that have been known for a long time. In addition, a recent study found that its leaves had anticonvulsant properties [17].
Congestive heart failure: A passion flower and hawthorn extract has been studied as a possible treatment for shortness of breath and difficulty exercising in patients with congestive heart failure. Although the findings are encouraging, the effects of passion flower alone are unknown. Before a strong recommendation can be made, high quality human research on passion flower alone in comparison to prescription drugs used for this condition is required.
Anticonvulsant activity: Current Anti Epileptic Drug (AED) therapy for epilepsy is associated with side effects, dose related and chronic toxicity, and teratogenic effects, and approximately 30% of patients continue to have seizures despite AED therapy. Natural products derived from ancient remedies have made significant contributions to the discovery of modern drugs and can serve as an alternative source for the development of AEDs with novel structures and improved safety and efficacy profiles. Evidence for anticonvulsant activity of P. incarnata in the pentylenetetrazole model clonic seizure has been tested. Because of P. incarnata's protective effects in clonic seizures, it is thought that it could be useful in the treatment of absent seizures. Furthermore, the importance of the benzodiazepine receptor in P. incarnata effects should be considered [18].
Antianxiety activity: Herbal medicines could be used to treat anxiety if they are proven to be effective and safe. One of these compounds is passion flower extract. P. incarnata has traditionally been used to treat anxiety and insomnia. A fraction derived from the methanol extract of P. incarnata was found to have good anxiolytic activity in mice using the Elevated Plus Maze (EPM) anxiety model. P. Incarnata's phytopharmacologically active constituent, with Benzoflavone as the basic moiety, is eagerly awaited. In rats, the potential anxiolytic effects of chrysin, a Passiflora extract, as well as the purported modulation of the benzodiazepine receptor on the GABA (A) receptor, were investigated. It has been proposed that chrysin reduces anxiety in rats by interfering with the GABA (A) receptor, as measured by elevated plus-maze, corticosterone, and catecholamine assays (Table 3).
| Sr. no. | Test | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HRSD): The HRSD has been criticised for clinical use because it focuses on insomnia rather than feelings of hopelessness, self-destructive thoughts, suicidal cognitions and actions. | Not depressed: 0–7 Mild (sub threshold): 8–13 Moderate (mild): 14–18 Severe (moderate): 19–22 Very severe (severe): >23 |
| 2 | Observers Assessment of Alertness and Sedation scale (OAA/S): The Observer's Assessment of Alertness/Sedation (OAA/S) Scale was created to assess the level of alertness in sedated subjects. This scale was tested in a three period crossover study on 18 subjects to determine its reliability as well as its criterion, behavioural, and construct validity. | A score of 3-4 on the OAA/S scale represents a moderate level of sedation analgesia and a score of 1-2 represents unconsciousness |
| 3 | Corah’s Dental Anxiety Scale, Revised (DAS-R): The Corah dental anxiety scale is a simple, easy to score test that a dentist can use to assess dental visit anxiety. It has also been demonstrated to be more inclusive, highly valid, and reliable. Thus, in the current study, the modified dental anxiety scale will be used to assess dental anxiety. | It’s a simple four question survey with five possible answers. 9 - 12 =moderate anxiety. 13-14= high anxiety. 15-20= severe anxiety |
| 4 | Ramsey scale: The goal of the study was to determine the validity and reliability of a new sedation score (Sedic score) for critically ill, sedated adult patients. | It divides a patient's level of sedation into six categories ranging from severe agitation to deep coma. Ramsay score between 6 and 10 = serious ceiling effect. |
| 5 | Digit Symbol Substitution Test (DSST): The DSST has been shown to be sensitive to changes in cognitive functioning in patients with major depressive disorder, and it holds promise as a clinical decision making tool for monitoring treatment effects in this and other cognition-related disorders. | To examine whether psychomotor speed predicts individual and combined disorders in cognition, mobility and mood and if white matter hyper intensities explain these associations. |
| 6 | Continuous Performance Task/Test (CPT): Continuous Performance Tasks (CPTs) are commonly used to obtain reliable parameters of behaviour, in which the subject performs a constant-difficulty task for minutes or tens of minutes without interruptions. | The most commonly used CPTs are the Test of Variables of Attention (TOVA), the Integrated Visual and Auditory CPT (IVA), and Conners’ CPT. These tests are often used for helping to support or rule out a diagnosis of ADHD. |
| 7 | Trieger Dot Test (TDT): The aiming test was specifically designed to assess speed as well as visio motor coordination. Patients had 90 seconds to place a dot in the centre of 300 circles with 2.5mm radius drawn on 1 cm graph paper. The number of circles that were centred in 90 seconds was recorded. | Trieger dot test measured hand eye coordination and is a simple paper pencil test requiring patients to connect 21 dots. Scoring is done by calculating number of dots missed. |
| 8 | Finger Tapping Test (FTT): The Finger Tapping Test (FTT) is a neuropsychological examination of motor functioning, specifically motor speed and lateralized coordination. The subject's palm should be immobile and flat on the board during administration, with fingers extended, and the index finder placed on the counting device. | The results of the first study into finger tapping speeds smokers little faster non smokers normal speed it people faster people who avoid exercise slow |
| 9 | State Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI): The State Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) is a popular tool for assessing trait and state anxiety. In clinical settings, it can be used to diagnose anxiety and distinguish it from depressive syndromes. It is also frequently used in research as a predictor of caregiver distress. | STAI varies from a minimum score of 20 to a maximum score of 80 no or low anxiety = 20-37 moderate anxiety = 38-44 high anxiety = 45-80 |
| 10 | Visual Analogue Scale (VAS): A Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) is a measurement instrument that attempts to measure a characteristic or attitude that is thought to range across a range of values and cannot be easily measured directly. It is frequently used in epidemiologic and clinical research to assess the severity or frequency of different symptoms. | The patient marks on the line the point that they feel represents their perception of their current state. The VAS score is determined by measuring in millimeters from the left hand end of the line to the point that the patient marks. |
| 11 | Memory test: Memory tests assess memory ability in the short and medium term. They are used to detect possible memory loss and the disease that causes it. Memory tests aid in the control, evaluation, and improvement of a person's memory. |
Table 3: Effect of Passiflora treatments on neuropsychiatric parameters.
Anti-cancer activity: It has been hypothesized that the phytochemical composition of passion fruit juice has valuable anti-cancer activity. Chrysin, a passion flower extract, may be beneficial due to its ability to reduce surgical suppression of Natural Killer (NK) cell activity, thereby reducing cancer metastatic spread [19].
Anti-tumor activity: The activity of gelatinase matrix metalloproteinase has been inhibited by fruit decoctions of various Passiflora species (MMP-2 and MMP-9). Two metallo proteases were discovered to be involved in tumor invasion, metastasis, and angiogenesis. The enzymes inhibited water extracts of P. edulis at various concentrations [20].
Sexual dysfunction: The isolation of a tri substituted benzoflavone moiety as the main phyto constituent of P. incarnata has been a promising breakthrough in elucidating the mode of action of this plant, which is mentioned in ancient Ayurveda medical writings as a promising cure for male impotence, postmenopausal decline in female libido, menstrual irregularity, morphine’s, alcoholism and tobacco addiction [21]. Furthermore, multiple studies have shown that it is more effective as a sedative and antispasmodic, in particular when combined with other drugs such as a passiflora extract, which significantly prolongs sleeping time when administered to rats. Bergner also claims that Passiflora extracts can be used to treat the manic phase of bipolar disorder, which is characterized by symptoms such as neuralgia and shingles, as well as fretfulness in teething children and other general pain. Passiflora has also been used to treat abnormal cardiac arrhythmias. Harmine's antileishmanicidal activities have recently received more attention. Leishmaniasis is a macrophage associated disease spread by infected sand flies bites [22,23].
Antioxidant activity: The antioxidant power of P. nitida leaf and P. palmeri stem extracts correlates with high catechin and odiphenol contents and shows antimicrobial activity. P. foetida leaf extracts, which also have high antimicrobial activity, have a low antioxidant capacity and low levels of o-diphenol and catechin. P. tenuifila leaves contain a high concentration of flavones and total phenols, but only a moderate amount of antioxidant activity, which is likely due to the lower contribution of o-diphenols and gallocatechins relative to the phenol content. P. edulis leaf and stem extracts were tested for antioxidant activity using the 1,1-Diphenyl-2-Picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free radical scavenging assay. DPPH provides a simple and accurate method for determining the oxidizable groups of natural or synthetic anti-oxidants [24].
Antimicrobial activity: Many of the chemical components of passion flower (passicol) have antimicrobial activity in Passiflora species. The ethanol leaf extracts had varying degrees of antibacterial activity against P. putida, V. cholerae, and S. flexneri and S. pyogenes, respectively. Acetone extracts were found to have strong to moderate activity against V. cholerae, P. putida, S. flexneri, and S. pyogenes. The ethanol fruit extracts had a moderate antibacterial activity against V. cholerae, P. putida, S. pyogenes, and S. flexneri. Among the two parts tested, leaf extracts outperformed fruits in terms of antibacterial activity 56. Earlier studies used various methods to investigate the antibacterial properties of Passiflora species. Passiflora has antibacterial activity against Pseudomonas tetrandra, Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Anti-inflammatory activity: In the in vivo experimental model, the aqueous leaves extract of Passiflora species exhibited potent anti-inflammatory action. On mice, the aqueous leaves extract of P. edulis has a significant antiinflammatory activity. In the acute model of inflammation caused by intrapleural injection of mice, systemic administration of P. edulis exhibited pronounced anti-inflammatory actions, characterized by inhibition of leukocyte influx to the pleural cavity and associated with significant blockade of myeloperoxidase, nitric oxide, TNF-, and IL-1 levels. In one experiment, P. edulis suppressed TNF and IL-1 levels more effectively than dexamethasone. As a result, P. edulis could be a source of new therapeutic candidates with a spectrum of activity similar to that of current anti-inflammatory steroids such as dexamethasone [25].
Conclusion
Various Passiflora species can be found all over the world. These studies suggest that this herbal treatment is a cutting edge choice for bio prospecting and drug development for the treatment of illnesses like anxiety, insomnia, convulsions, sexual dysfunction, cough, cancer, and postmenopausal syndrome. There are still many chances for research into the more recent functions of this plant as well as its therapeutic benefits. The chemical components are fully described in this review. Some neuropsychiatric problems may be improved by passionflower. Administration of passionflower has not been connected to any side effects, including memory loss or the breakdown of psychometric capabilities. Similar to medications like oxazepam or midazolam, Passiflora incarnata provides a calming effect. It therefore seems to be a secure and efficient medication for lowering stress reactivity, sleeplessness, anxiety, and depressive like behaviours.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Management and Principal of GES Sir Dr. M. S. Gosavi College of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, Nashik-422003 MS, India for providing all necessary facility to carry out this work.
Conflict of interest
Author declares no conflict of interest
References
- Dhawan K, Dhawan S, Sharma A (2004) Passiflora: A review update. J Ethnopharmacol 94:1-23
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Ingale SP, Kasture SB (2017) Protective effect of standardized extract of Passiflora incarnata flower in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease. Anc Sci Life 36:200-206
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Akhondzadeh S, Naghavi HR, Vazirian M, ShayeganpourA, Rashidi H, et al. (2001) Passionflower in the treatment of generalized anxiety: A pilot double blind randomized controlled trial with oxazepam. J Clin Pharm Ther 26:363-367
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Reginatto FH, de Paris F, Petry RD, Quevedo J, Ortega GG, et al. (2006) Evaluation of anxiolytic activity of spray dried powders of two South Brazilian Passiflora species. Phytother Res 20:348-351
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Wheatley D (2005) Medicinal plants for insomnia: A review of their pharmacology, efficacy and tolerability. J Psychopharmacol 19:414-421
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Akhondzadeh S, Kashani L, Mobaseri M, Hosseini SH, Nikzad S, et al. (2001) Passion flower in the treatment of opiates withdrawal:A double blind randomized controlled trial. J Clin Pharm Ther 26:369-373
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Nassiri-Asl M, Shariati-Rad F, Zamansoltani F (2007) Anticonvulsant effects of arial parts of Passiflora incarnata extract in mice: Involvement of benzodiazepine and opioid receptors. BMC Complement Altern Med 7:1-6
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Tiwari S, Singh S, Tripathi S, Kumar S (2015) A pharmacological review: Passiflora species. Asian J Pharm Res 5:195-202
- Hidalgo IJ, Raub TJ, Borchardt RT (1989) Characterization of the human colon carcinoma cell line (caco-2) as a model system for intestinal epithelial permeability. Gastroenterology 96:736-749
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Press B, Di Grandi D (2008) Permeability for intestinal absorption: Caco-2 assay and related issues. Curr Drug Metab 9:893-900
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Cecchelli R, Berezowski V, Lundquist S, Culot M, Renftel M, et al. (2007) Modelling of the blood brain barrier in drug discovery and development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:650-661
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Ingale SP, Kasture SB (2012) Psychopharmacological profile of Passiflora Incarnata Linn in mice. Int J Phytopharmacol 3:263-268
- Ichimura T, Yamanaka A, Ichiba T, Toyokawa T, Kamada Y, et al. (2006) Antihypertensive effect of an extract of Passiflora edulis rind in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 70:718-721
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Nassiri-Asl M, Shariati-Rad S, Zamansoltani F (2007) Anticonvulsant effects of aerial parts of Passiflora incarnata extract in mice: involvement of benzodiazepine and opioid receptors. BMC Complement Altern Med 7:1-6
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Akhondzadeh S, Naghavi HR, Vazirian M, Shayeganpour A, Rashidi H, et al. (2001) Passion flower in the treatment of generalized anxiety: A pilot double blind randomized controlled trial with oxazepam. J Clin Pharm Ther 26:363-367
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Patel SS, Saleem TM, Ravi V, Shrestha B, Verma NK, et al. (2009) Passiflora incarnata Linn: A phytopharmacological review. Int J Green Pharm (IJGP) 3:277-280
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Rowe CA, Nantz MP, DeNiera C, Green K, Talcott ST, et al. (2004) Inhibition of neoplastic transformation of benzo (α) pyrene treated BALB/c 3T3 murine cells by a phytochemical extract of passionfruit juice. J Med Food 7:402-407
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Janda K, Wojtkowska K, Jakubczyk K, Antoniewicz J, Skonieczna-Ã
»ydecka K (2020) Passiflora incarnata in neuropsychiatric disorders a systematic review. Nutrients 12:3894
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Mark Jr TM, Reginald Hills BS, Dixon P (2008) The effects of chrysin, a Passiflora incarnata extract, on natural killer cell activity in male Sprague Dawley rats undergoing abdominal surgery. AANA J 76:113
[Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Patel S, Verma N, Gauthaman K (2009) Passiflora incarnata Linn: A review on morphology, phytochemistry and pharmacological aspects. Pharmacogn Rev 3: 175-181
[Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Kim M, Lim HS, Lee HH, Kim TH (2017) Role identification of Passiflora Incarnata Linnaeus: a mini review. J Menopausal Med 23:156-159
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Dhawan K, Sharma A (2003) Restoration of chronicâ?ÂΔ9â?ÂTHCâ?Âinduced decline in sexuality in male rats by a novel benzoflavone moiety from Passiflora incarnata Linn. Br J Pharmacol 138:117-120
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Kinghorn GR (2001) Passion, stigma, and STI. Sex Transm Infect 77:370-375
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Michael HS, Mohammed NB, Ponnusamy S, Gnanaraj WE, Michael HS (2022) A Folk Medicine: Passiflora incarnata L–Phytochemical Profile with Antioxidant Potency. Turk J Pharm Sci 19:287-292
[Crossref] [Googlescholar] [Indexed]
- Kamal SA, Mohammed GJ, Hameed IH (2018) Antimicrobial, Anti-inflammatory, Analgesic Potential and Cytotoxic Activity of Salvadora persica: A review. Indian J Public Health Res Dev 9:393-398
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences